Nature has evolved efficient strategies to synthesize complex mineralized structures that exhibit exceptional damage tolerance. One such example is found in the hypermineralized hammer-like dactyl clubs of the stomatopods, a group of highly aggressive marine crustaceans. The dactyl clubs from one species, Odontodactylus scyllarus, exhibit an impressive set of characteristics adapted for surviving high-velocity impacts on the heavily mineralized prey on which they feed. Consisting of a multiphase composite of oriented crystalline hydroxyapatite and amorphous calcium phosphate and carbonate, in conjunction with a highly expanded helicoidal organization of the fibrillar chitinous organic matrix, these structures display several effective lines of defense against catastrophic failure during repetitive high-energy loading events.
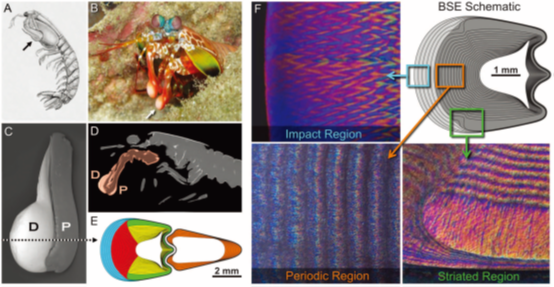
Morphological features of the stomatopod dactyl club
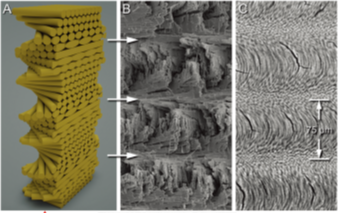
Chitin fibril helicoidal structural motif within the periodic region (with periodicity: ~75 mm). Comparisons between a generalized threedimensional model of a helicoid (A) with an SEM fractograph (B) and a polished surface from a transverse cross section (C)
Information Source: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/336/6086/1275

