引文信息:
Chao Xu, Xiang Chen, Wenzheng Wu, Qingping Liu & Luquan Ren . Bioinspired Multi-Metal Structures Produced via Direct Ink Writing. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2022, 19(6),1578–1588.
Bioinspired Multi-Metal Structures Produced via Direct Ink Writing
Chao Xu, Xiang Chen, Wenzheng Wu, Qingping Liu & Luquan Ren
1 Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering (Ministry of Education), Jilin University, Changchun, 130000, China
2 Weihai Institute of Bionics, Jilin University, Weihai, 264400, China
3 School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Jilin University, Changchun, 130000, China
Abstract
Bioinspired Multi-Metal Structures (MMSs) combine distinct properties of multiple materials, benefiting from improved properties and providing superior designs. Additive Manufacturing (AM) exhibits enormous advantages in applying different materials and geometries according to the desired functions at specific locations of the structure, having great potential in fabricating multi-materials structures. However, current AM techniques have difficulty manufacturing 3D MMSs without material cross-contamination flexibly and reliably. This study demonstrates a reliable, fast, and flexible direct ink writing method to fabricate 3D MMSs. The in-situ material-switching system enables the deposition of multiple metallic materials across different layers and within the same layer. 3D Fe–Cu MMSs with complex geometries and fine details are fabricated as proof of concept. The microstructures, chemical and phase compositions, and tensile fracture surfaces of the Fe–Cu interfaces indicate a well-bonded interface without cracks, delamination, or material cross-contamination. We envision this novel method making other metallic combinations and even metal-ceramic components. It paves the way for manufacturing 3D MMSs using AM and establishes the possibilities of numerous MMSs applications in engineering fields.
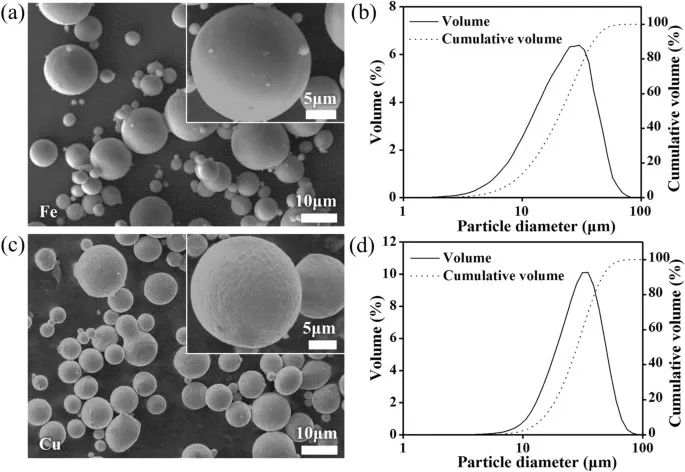
Fig. W1 a SEM images and b PSD of the Fe powder, c SEM images and d PSD of the Cu powder
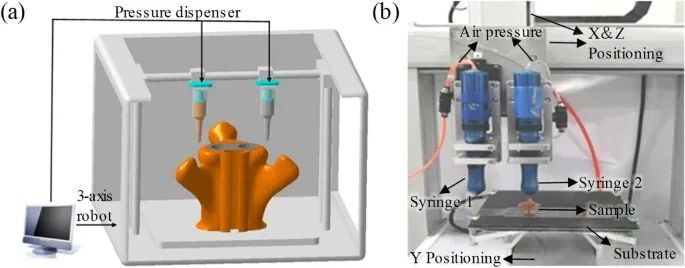
Fig. W2 a Schematic and b basic setup of the multiple-material DIW 3D printer consisting of duel ink syringes, 3-axis stage and a pressure dispensing system
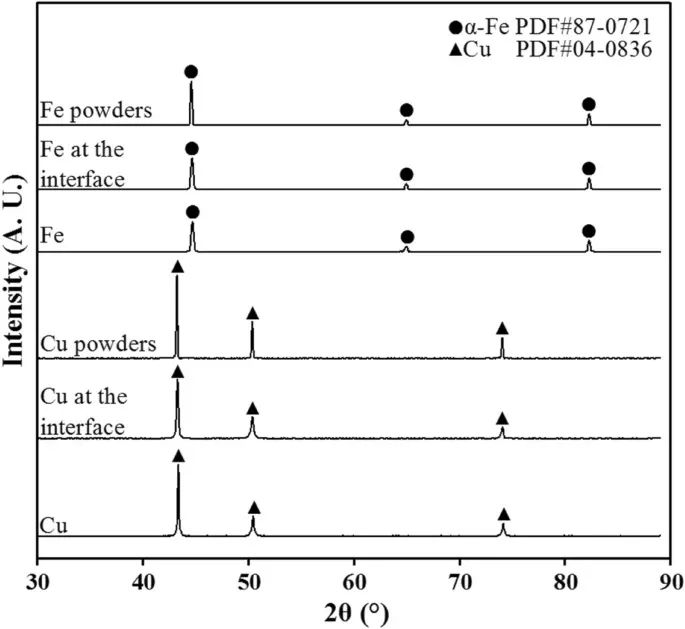
Fig. W3 XRD results of Fe and Cu raw powders, Fe and Cu at interfaces, and Fe and Cu zones of the Fe–Cu MMS

Fig. W4 SEM images of tensile fracture surfaces of the a Fe, b Cu, and c Fe–Cu interdigital structures fabricated via DIW and subsequent sintering
以上文章转载于微信公众号国际仿生工程学会,如有侵权,请及时联系我们修改或进行删除。
Information Publisher: Chao Xu, Xiang Chen, Wenzheng Wu, Qingping Liu & Luquan Ren
Information Release Unit: Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering (Ministry of Education), Jilin University,
Information Source: https://rdcu.be/cYrnM

