引文信息:
Chaofeng Chen, Zhijiang Du, Long He, Yongjun Shi, Jiaqi Wang, Wei Dong. A Novel Gait Pattern Recognition Method Based on LSTM-CNN for Lower Limb Exoskeleton. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2021, 18(5), 1059-1072.
A Novel Gait Pattern Recognition Method Based on LSTM-CNN for Lower Limb Exoskeleton
1、Chaofeng Chen, Zhijiang Du,Long He, Yongjun Shi, Jiaqi Wang, Wei Dong State Key Laboratory of Robotics and System, Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT), Harbin 150001, China
2、China South Industries Group Corporation, Weapon Equipment Research Institute, Beijing 102202, China
Abstract
This paper describes a novel gait pattern recognition method based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) and Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for lower limb exoskeleton. The Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) installed on the exoskeleton to collect motion information, which is used for LSTM-CNN input. This article considers five common gait patterns, including walking, going up stairs, going down stairs, sitting down, and standing up. In the LSTM-CNN model, the LSTM layer is used to process temporal sequences and the CNN layer is used to extract features. To optimize the deep neural network structure proposed in this paper, some hyperparameter selection experiments were carried out. In addition, to verify the superiority of the proposed recognition method, the method is compared with several common methods such as LSTM, CNN and SVM. The results show that the average recognition accuracy can reach 97.78%, which has a good recognition effect. Finally, according to the experimental results of gait pattern switching, the proposed method can identify the switching gait pattern in time, which shows that it has good real-time performance.
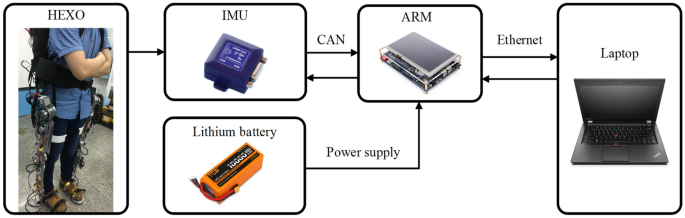
Fig. W1 Schematic diagram of data acquisition system.
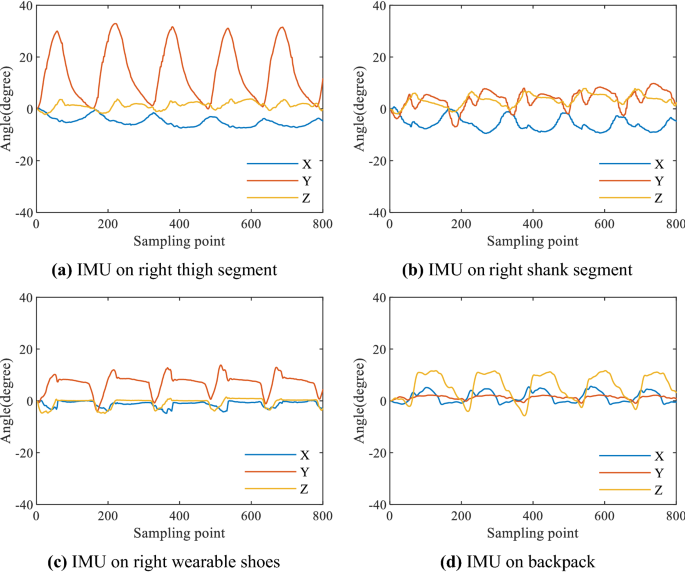
Fig. W2 The information collected by the IMUs on each part of the HEXO during walking gait.
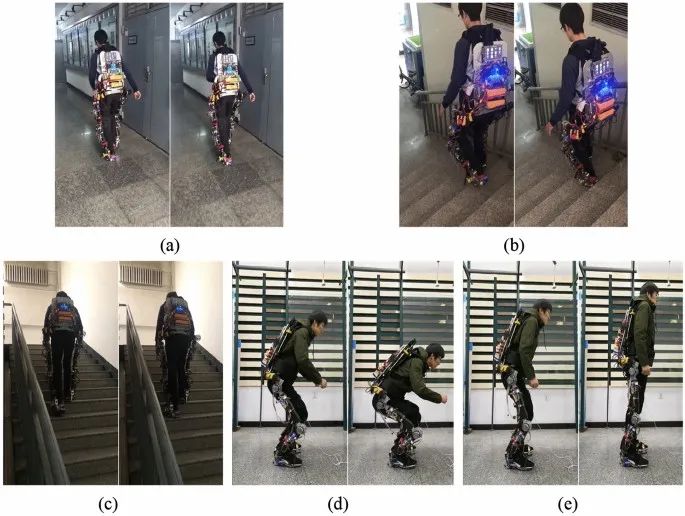
Fig. W3 The subject wears exoskeleton and moves in different gait pattern. A Walking; B up stairs; C down stairs; D sitting down; E standing uptrol.
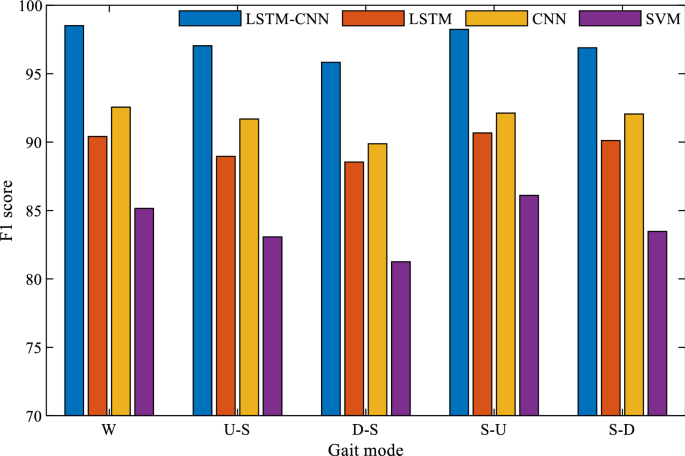
Fig. W4 F1 score comparison between different gait mode identification models.
Information Publisher: Chaofeng Chen, Zhijiang Du, Long He, Yongjun Shi, Jiaqi Wang, Wei Dong
Information Release Unit: Wei Dong State Key Laboratory of Robotics and System, Harbin Institute of Technology (HIT)
Information Source: https://rdcu.be/cBJ9W

