引文信息:
Long Bai, Hao Wang, Xiaohong Chen, Jia Zheng, Liming Xin, Yupeng Deng & Yuanxi Sun. Design and Experiment of a Deformable Bird-inspired UAV Perching Mechanism. Journal of Bionic Engineering, 2021, 18(6), 1304–1316
Design and Experiment of a Deformable Bird-inspired UAV Perching Mechanism
Long Bai, Hao Wang, Xiaohong Chen, Jia Zheng, Liming Xin, Yupeng Deng & Yuanxi Sun
State Key Laboratory of Mechanical Transmission, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 400030, China
Abstract
Energy consumption and acoustic noise can be significantly reduced through perching in the sustained flights of small Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). However, the existing flying perching robots lack good adaptability or loading capacity in unstructured environments. Aiming at solving these problems, a deformable UAV perching mechanism with strong adaptability and high loading capacity, which is inspired by the structure and movements of birds' feet, is presented in this paper. Three elastic toes, an inverted crank slider mechanism used to realize the opening and closing movements, and a gear mechanism used to deform between two configurations are included in this mechanism. With experiments on its performance towards different objects, Results show that it can perch on various objects reliably, and its payload is more than 15 times its weight. By integrating it with a quadcopter, it can perch on different types of targets in outdoor environments, such as tree branches, cables, eaves, and spherical lamps. In addition, the energy consumption of the UAV perching system when perching on objects can be reduced to 0.015 times that of hovering.
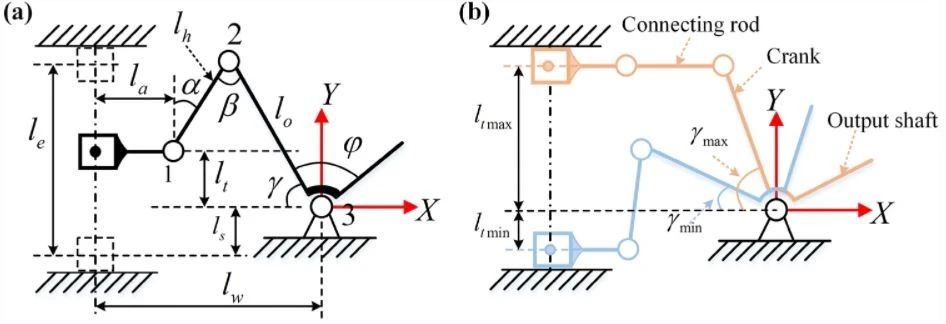
Fig. W1 Diagram of the inverted crank slider mechanism. a Some important parameters are displayed in this diagram. b The states of two extreme positions
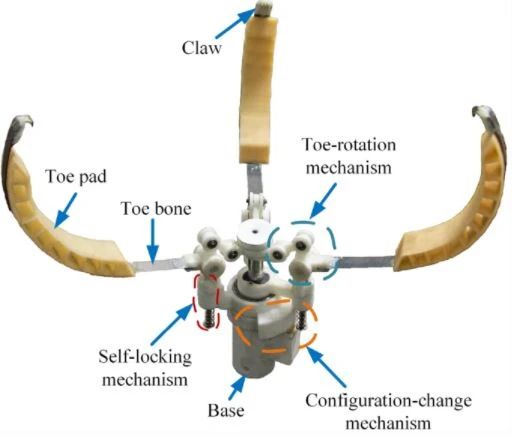
Fig. W2 The prototype of the perching mechanism. It includes three elastic toes composed of toe pads, toe bones and claws, a toe–rotation mechanism that mainly depends on an inverted crank slider mechanism, a configuration-change mechanism that depends on a gear mechanism, a self-locking mechanism, and a base
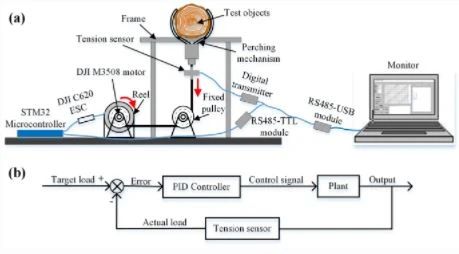
Fig. W3 Test platform and control strategy of the perching mechanism. a The perching mechanism grabs the test objects. Then, it is loaded by a motor through a rope, and the loading value is measured by a tension sensor and recorded by a monitor. b The PID controller is used to control the loading value
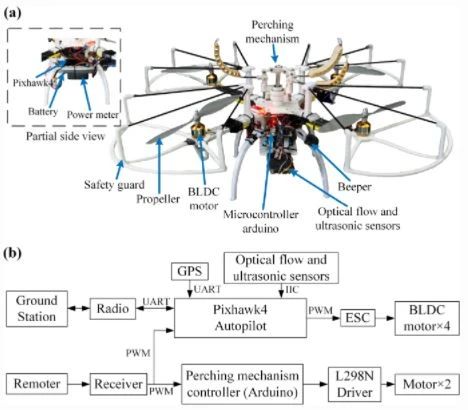
Fig. W4 Prototype and hardware structure of the system. a The prototype of the integrated flight-perching robot. b The system's hardware structure. It's mainly composed of two parts, the flight system and the perching system
Information Publisher: Long Bai, Hao Wang, Xiaohong Chen, Jia Zheng, Liming Xin, Yupeng Deng & Yuanxi Sun
Information Release Unit: Chongqing University
Information Source: https://rdcu.be/cDwKU

